References
Prodigy. Parkinson's disease. Newcastle upon Tyne: PRODIGY; 2005.
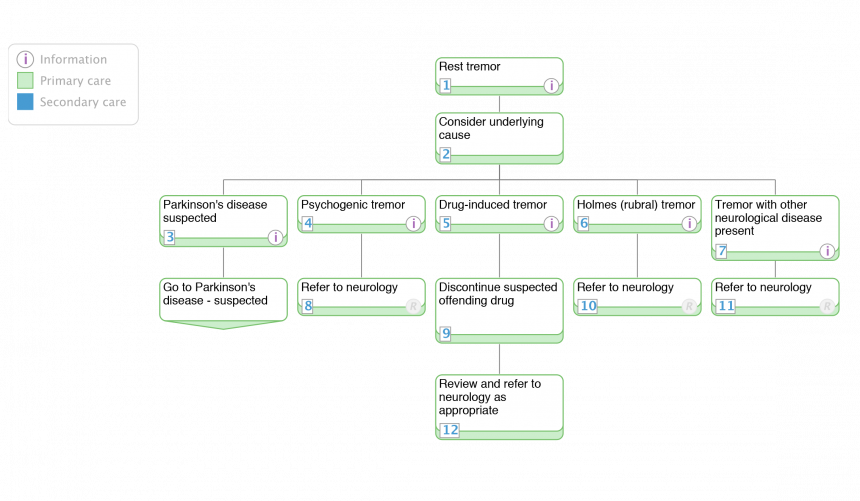
1. Rest tremor
Quick info:
Scope:
- this page provides information on the different causes of rest tremor Definition:
- rest tremor is present in a body part that is not voluntarily activated and is completely supported against gravity
- often caused by Parkinson's disease and other causes of parkinsonism
- however other causes of rest tremor should be considered Features of Parkinson's disease:
- typical unilateral onset of tremor in hand and occasionally a leg
- "pill rolling tremor" rare but a characteristic of Parkinson's disease
- rest tremor present in 70% of Parkinson's disease patients (practical tip - to induce rest tremor ask patient to count down from 10 out loud)
- Look for
- facial or vocal impassivity
- reduced arm swing on walking and shoulder shrug test (look for arm swing whilst shaking patient's shoulders)
- cogwheel rigidity
- bradykinesia
- micrographia
- postural instability
- refer to a person with expertise in Parkinson's disease prior to instigating medication Main causes:
- Parkinson's disease (see pathway)
- other causes of parkinsonism
- drug-induced tremor
- dystonic tremor syndromes
- severe essential tremor
- Holmes tremor (also termed rubral)
- psychogenic tremor
- Wilson's disease
- vascular parkinsonism - multiple system atrophy, progressive supranuclear palsy
- drug induced parkinsonism - phenothiazines, metoclopramide, hydrocephalus, encephalitis, toxicity (eg. manganese) Investigations:
- routine biochemistry, including thyroid function, liver function tests, calcium & phosphate
- Other possible investigations:
- to rule out Wilson's diseasecopper studies if <50 years old at onset, but still consider if >50 years
- dopamine transporter scan
- consider genetic tests in appropriate cases
- in young people (less than age 30 years) consider diagnostic studies to rule out Wilson's disease
2. Parkinson's disease suspected
Quick info:
Features of Parkinson's disease
- typical unilateral onset of tremor in a hand and occasionally a leg
- "pill rolling tremor" rare but characteristic of Parkinson's disease
- rest tremor present in 70% of Parkinson's disease patients (practical tip - to induce rest tremor ask patient to count down from 10 out loud)
- Look for:
- facial or vocal impassivity
- reduced arm swing on walking and shoulder shrug test
- cogwheel rigidity
- bradykinesia (slow movements with decrement)
- micrographia
- postural instability
- refer to a person with expertise in Parkinson's disease prior to instigating medication
3. Psychogenic tremor
Quick info:
The following are clues to a psychogenic aetiology:
- history:
- sudden onset, remissions or both
- unusual combinations of rest, postural or intention tremors
- somatization in past medical history
- consider medical causes for tremor with psychiatric illness (eg. Wilson's disease)
- Examination:
- decreased tremor amplitude during distraction
- variations in tremor frequency with distractions or voluntary movements of the other hand (entrainment)
- co-activation sign of psychogenic tremor (tremor only present when arm is voluntarily stiffened)
- appearance of additional and unrelated neurological signs
- finger tremor is unusual in psychogenic tremor
- simple reflex time studies
- consider other causes of tremor
- focus of treatment should be predominantly psychological
4. Drug-induced tremor
Quick info:
- can be caused by numerous drugs or drug withdrawal
- usually presents as postural tremor, but rest and/or intention tremors may occur
- Commonly associated with:
- alcohol
- sympathomimetics
- bronchodilators - â2 agonists
- theophylline
- caffeine
- dopamine
- epinephrine and norepinephrine
- lithium
- sodium valproate
- antipsychotic medication
- anti-emetics (metoclopramide, prochlorperazine)
- tricyclic antidepressants
- corticosteroids
- any drug with a primary effect on the central nervous system can produce tremor as a side-effect
5. Holmes (rubral) tremor
Quick info:
- Typically three tremor components are present: rest, postural tremorand intention tremor
- often severe. The action tremor severity is usually greater than that of the rest component
- slow (frequency <4.5Hz) irregular tremor
- tends to involve proximal (action tremor) and distal (rest tremor) muscles
- Holmes tremor has numerous causes including stroke, vascular malformations, tumours, head injury, toxoplasmosis, major tranquilizers, radiation)
- typically 2 weeks to 2 years delay from causal lesion to tremor onset
- lesions typically sited in midbrain or thalamus
- structural imaging (MRI scan) recommended
- dopamine transporter scan often abnormal
- multiple sclerosis is a rare cause of Holmes tremor
6. Tremor with other neurological disease present
Quick info:
- multiple sclerosis (predominantly postural and intention tremor)
- peripheral neuropathy (predominantly postural and intention tremor)
- Wilson's disease
- hereditary ataxia












